


The shift in the way customers want to interact with financial services is driving the FinTech industry to digitize more and more services and setting the future of banking technology. Digital banking software is one of the FinTech solutions customers most commonly use in their daily lives. In this article, we’ll focus on the technical means to develop and improve digital banking software. Beginning with a robust digital banking platform architecture, technical stack, API integrations, and finishing with the implementation of advanced technologies. In particular, in terms of digital banking reference architecture development, we’ll cover microservices in banking and financial services along with core banking microservices. Your steps to creating a web or mobile banking system architecture should be reasoned and well-defined for all the stakeholders.


Learn about the perfect balance between compliance and innovation, discuss risk mitigation and future-proofing strategies, and much more!
We have expertise in developing BaaS, wealth management, and other FinTech solutions
The primary aim of digitization of banking is to build reliable solutions that can win the trust of customers and convince them that digital banking is safe and convenient. According to a 2021 Lightico survey among 1,037 consumers globally, 56.9 percent still think that face-to-face banking interactions are the most secure and reliable. And when those same consumers actually decide to try online banking services, there are instances when they’re still required to visit a bank in person to sign something by hand. Lightico reports that 36 percent of respondents find such situations very frustrating.
Emerging digital banking startups aspire for a completely different look and feel from traditional banking. However, while digital startups can excel in terms of customer experience, they can still draw on the profitability strategies of traditional banks to find a stable place in the financial market. Funds raised from investors cannot be the only source of money for starting a digital bank.
Thus, it’s best to start building robust digital banking software with the traditional banking business model in mind, primarily in terms of security. Your business goal, monetization strategies, and business and functional requirements will largely predetermine your:
Further on, we’ll pay attention to each of the above-mentioned technical aspects in terms of core banking software development and modernization. Let’s begin with digital banking architectures.
What it takes for a traditional banking institution to go digital
Covering the topic of microservices in banking and financial services, we’ll discuss two common types of digital banking software architectures: layered and microservices-based.
A typical layered mobile banking system architecture consists of three layers:
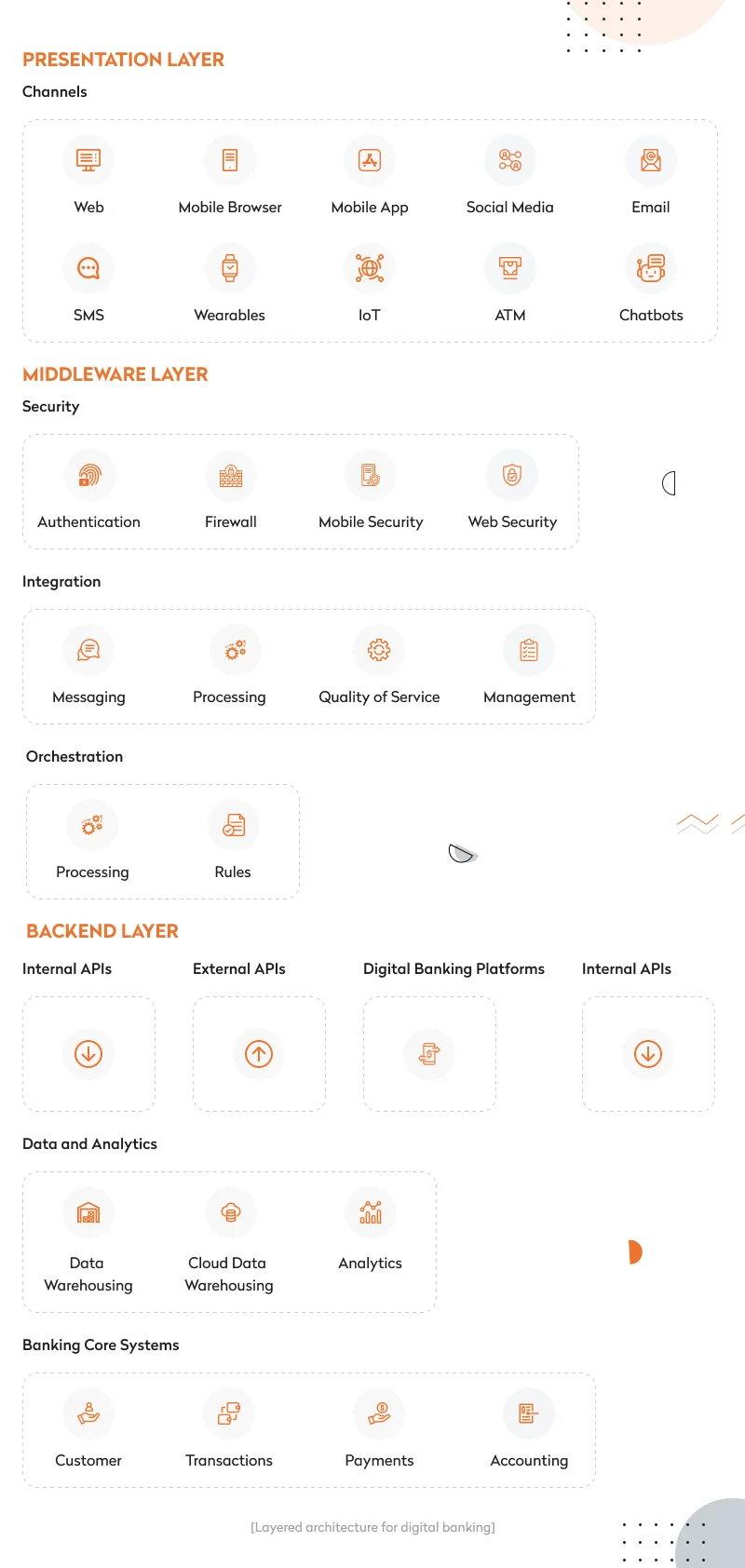
The presentation layer (front end) enables customers’ interactions with the banking software. The front end of technology banking solutions includes web and mobile banking apps, chatbots, and software for IoT devices and wearables. The presentation layer handles the browser and user interface communication logic.
The middleware layer includes three sublayers:
The backend layer includes the following components:
Another common digital banking architecture is a microservices architecture.
Many digital banks choose to build their banking software on a microservices architecture, as it offers the greatest scalability opportunities and allows for many integrations with third-party services. If open banking is your go-to, microservices architecture in banking can be the right option for you. Plus, with a microservices digital banking architecture, you have more flexibility as you can control which functionalities to add or enhance and when. Check out our case study on how we ensured successful migration for a logistics company from a monolithic architecture to microservices.
However, it can be challenging to maintain a microservices architecture in banking if you aren’t planning to scale your solution (both in terms of functionality and your client base) in the long-term perspective or if you’re only beginning to develop banking software. In such cases, a layered digital banking architecture can be more advantageous.
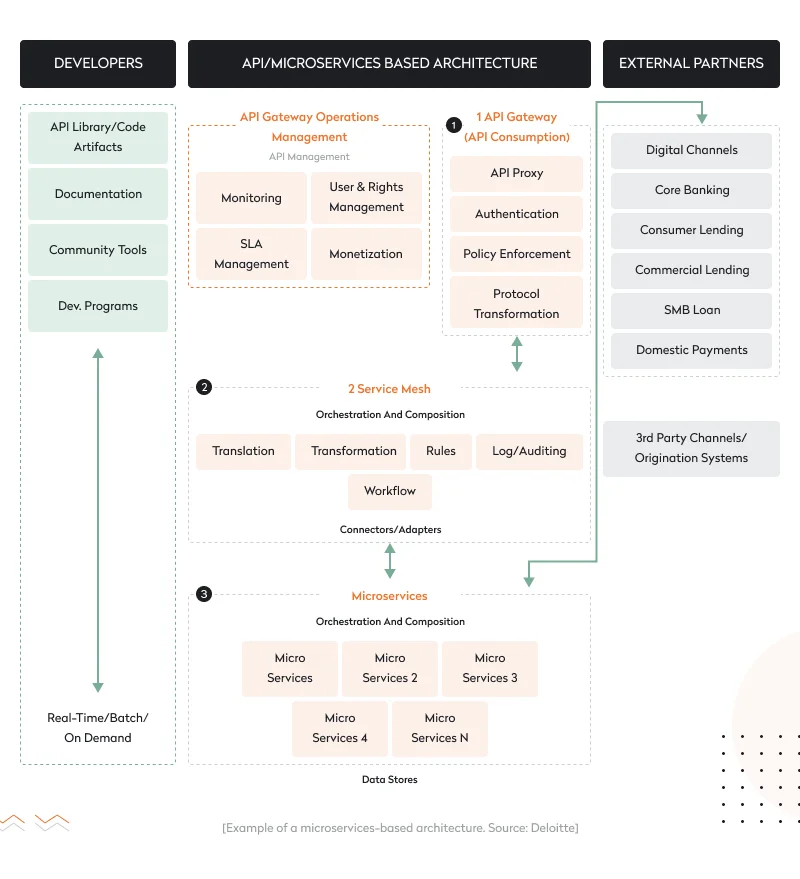
A microservices digital banking platform architecture consists of three critical components:
Your choice of core banking software architecture depends on your goals and your vision for your software’s future development. With the growing pressure of global digital transformation, core banking microservices appear to be the most adaptable architecture in terms of acquiring disruptive technologies. However, architecture design is a highly individual thing. And it may be that the best architecture for you is a combination of two or more different architectural types.
Thus, to ensure a suitable solution architecture during your finance software development, you’ll need to work with a skilled solution architect to perform all necessary analyses of your business and functional requirements. Once your solution is built, further architecture assessments will ensure that your software stays up to date, offers stable performance, and meets your changing business needs and requirements.
For example, the Australian neobank Xinja decided to shift from a service-oriented architecture (SOA) to an event-sourcing microservices architecture. The bank’s management decided not to buy an out-of-the-box solution but rather build this architecture from scratch to ensure maximum flexibility and integration capabilities.
Xinja didn’t choose the cheapest and quickest approach, but in the long run, it paid off. Connecting to Apple Pay, for instance, is a big and difficult project and may take a bank up to a year. With a robust microservices architecture in place, Xinja managed to integrate Apple Pay in five weeks instead of months.
After choosing your digital banking platform architecture, another important technical aspect of developing digital banking software solutions is ensuring its security.
FinTech service companies work with sensitive customer information, so security for digital financial services is of the utmost importance. This is made clear by the fact that apart from PCI DSS, practically every country has its own additional security compliance requirements regarding digital identity, data protection, and cybersecurity.
On April 1, 2022, a final rule went into effect in the US that obliges banking organizations to notify a primary federal regulator within 36 hours in case of any cybersecurity threat. Bank service providers also have to notify customers as soon as possible in case of any incident. Denmark has introduced a new and more secure digital identity infrastructure called MitID to replace its predecessor, NetID. MitID will be used to approve online shopping payments, online bank logins, and logins to skat.dk for taxes. This solution will launch in the summer of 2022.
It’s also important to remember that in some instances, digital and traditional banks may be subject to different requirements. So it’s necessary to always monitor compliance requirements that appear in your markets to stay in the loop and know how you may need to modify your security measures. Further on, we’ll discuss all the common criteria and aspects of digital banking security.
OAuth 2.0 protocol benefits for digital banking
OAuth 2.0 is a common protocol that ensures a high level of security during authentication and authorization. This protocol acts as an identity provider, allowing third-party developers to build apps on top of it. One of its key principles is that APIs will only redirect users to a URL that was previously registered with the service. This helps to prevent redirection attacks where an authorization code or access token can be intercepted by an attacker. Among others, OAuth 2.0 is used by Fortune 500 companies including Google, Microsoft, Facebook, Amazon, and Twitter. Benefits OAuth 2.0 provides for developers include:
Ensuring secure encryption and data storage systems
To mitigate risks and make sure your users’ data is transmitted and stored securely, stick to industry-proven and government-approved cryptographic algorithms (like the Advanced Encryption Standard with 256-bit keys), modes, and libraries. Follow the latest community best practices and use reliable cryptography standards to ensure cipher configurations and block modes are set up securely. Last but not least, keep sensitive private data encrypted with a managed key while it’s transferred and at rest to ensure data integrity and confidentiality at all steps. At Yalantis, we follow recommendations for cryptographic key management (including NIST SP 800-57) to eliminate common security risks including key reuse, weak keys, and non-rotation.
Making the most of know your customer (KYC) and know your business (KYB) principles
KYC and KYB oblige financial organizations dealing with private or business money to verify the identity of counterparties before conducting financial transactions. Simply put, KYC and KYB is a system that contains a chain of third-party services that analyze users’ data to detect fraud at early stages. KYC and KYB principles along with identity verification, credit decisions, and ongoing transaction monitoring can serve as a risk management engine within digital banking software.
Establishing a dedicated fraud prevention department
This is a vital step to successfully detect and disarm cybercriminals before they actually commit a crime. For example, a fraud department can spot that a user is making online transactions with the same value from different IP addresses within one hour and block the account in question as suspicious. Fraud department employees use dedicated technologies and services to ensure your software’s security. To be proactive, they need dedicated tools and integrations with third-party services.
Developing security tools and setting up integrations lies on your technology partner’s (either in-house or outsourcing) shoulders. In the long run, establishing a fraud prevention department contributes to minimizing the risk of cybercrimes, which is definitely an investment in your bank’s good reputation and stability.
Choosing digital banking technologies is another serious task. In the next section, we discuss the factors that should influence your choice.
To choose the right technology stack for a banking application, you should place your business plan at the center, which means there are no one-size-fits-all solutions. You also want to consider two important aspects: your budget and core competencies within your team.
When addressing the business needs of your digital banking platform with technologies, there are certain criteria to consider.

When it comes to the banking industry technology stack, it’s important for your software development team to choose a target programming language and core framework based on their expertise. This way the whole development team will be on the same page and the development process will run smoothly.
These criteria can be expanded as the technology stack creates dependencies you’ll need to follow throughout the development process. To make the right choices, make sure to select a service provider that puts your business needs first and understands domain-specific app requirements.
If a digital banking solution integrates with diverse third-party services including for exchanging data with other banks, customers can get all-around banking and financial services and have a convenient user experience within one software system.
For example, the US SMB neobank Novo provides APIs for more than 1,000 applications and services. Primarily, these integrations relate to functionality that Novo doesn’t have yet like point-of-sale payments, invoices, payroll management, and ecommerce operations.
This approach forms a perfect ground for a flexible financial environment that could be otherwise called open banking. Open banking allows for sharing a customer’s financial information via open APIs. Customers can, for instance, integrate bank accounts with services that track finances, monitor savings plans, and access account management services to get insights into their overall financial capabilities and have a complete understanding of their finances. However, it’s important for these services to be reliable and trustworthy so customers can be sure their data is secure.
According to a YouGov and Tink 2021 survey among 308 financial executives, 68 percent of respondents increased their interest in open banking during the pandemic.
Talking about core banking software architecture, let’s cover open banking benefits for digital banking:

For example, the UK-based mobile banking application Starling offers a whole marketplace of bank systems & technology services inside its app that are powered by APIs. Customers can easily access loyalty, savings, insurance, or investment products. Back in 2019, Starling won a reward for the best online banking strategy, beating such companies as Monzo, Revolut, and Santander. The main reason Starling is successful in open banking is due to their constantly listening to customer feedback and adjusting their solutions accordingly.
Either in the first development stages or later, you can consider adding new banking technology solutions that can elevate your software performance, make your software more profitable, and make it more useful for your customers. But let’s discuss a few advanced solutions that are worthy of your attention.
This section is meant to show which solutions are at the top right now and are forming the future of technology in the banking industry.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning
The prolific use of AI and machine learning across diverse industries proves these technologies are here to stay. According to McKinsey, AI can generate $1 trillion in value for the banking industry annually. AI can be implemented for front, middle, and back office tasks. AI and machine learning can be used to:
For instance, the Czech startup Resistant AI is based on AI and machine learning to provide financial institutions with anti-fraud security products. Machine learning algorithms define fraudulent documents, while AI is used for spotting issues during transactions.
Blockchain
Decentralized finance (DeFi) based on blockchain technology is a common FinTech solution. DeFi’s primary aim is to eliminate intermediaries and centralized institutions from financial transactions. This solution is built on smart contracts, which are the digital equivalent of physical contracts.
Two common DeFi products are lending and borrowing protocols. DeFi enables peer-to-peer lending and borrowing of crypto assets, removing intermediaries from the equation. Thus, DeFi allows users to quickly get loans thanks to smart contracts. Blockchain-enabled solutions also allow customers to have more control over their assets, reducing instances of cyberattacks.
Robotic process automation (RPA)
RPA allows for the automation of monotonous tasks that have a simple procedure but take up lots of time if performed manually. Instead of people, bots can be programmed to perform these tasks. For example, bots can analyze documents that customers send for loan origination and extract all necessary information and validate it. RPA can also complement other processes including:
On a daily basis, the banking industry deals with lots of repetitive tasks that can be easily automated, saving time for employees and improving customer satisfaction thanks to quick service delivery.
To develop successful digital banking software, you’ll need to find your perfect balance in the technology stack, mobile banking system architecture design, APIs, and advanced technologies. Our team can guide you on this path to ensure that you manage to reach your goal. When deciding on the development strategy for digital banking solutions, we take into account all constraints you may have, such as time, budget, and scope. Still, we always focus on delivering maximum value to you and your customers.